Creating shadows in Photoshop is an essential skill that can significantly enhance the realism and depth of your images. Whether you’re editing photos for a professional project or just for fun, mastering shadow creation can take your work to the next level. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process step-by-step, ensuring even beginners can achieve stunning results.
Understanding Shadows
Before diving into Photoshop, it’s crucial to understand what shadows are and how they work. Shadows are created when an object blocks a light source, resulting in an area of darkness on a surface. Shadows can provide context about the light source’s position, distance, and intensity, making them a powerful tool for adding realism to digital images.
Types of Shadows
- Cast Shadows: These are the shadows that an object casts onto another surface. They can vary in sharpness and intensity based on the light source.
- Form Shadows: These are the shadows on the object itself, caused by its three-dimensional form and the light source direction.
Shadow Creation : Step by Step Guide
Step 1: Open Your Image in Photoshop
First, open Photoshop and load the image you want to work with. You can do this by going to File > Open and selecting your image file.
Step 2: Duplicate the Layer
It’s always a good idea to work on a duplicate layer to preserve the original image. Duplicate the background layer by right-clicking on it in the Layers panel and selecting Duplicate Layer. You can also use the shortcut Ctrl+J (Cmd+J on Mac).
Step 3: Isolate the Object
To create a realistic shadow, you need to isolate the object you want to cast the shadow. Use the Pen Tool (P) or any selection tool like the Quick Selection Tool (W) or Lasso Tool (L) to carefully select your object. Once selected, create a new layer with the object by pressing Ctrl+J (Cmd+J on Mac).
Creating Cast Shadows
Step 4: Create a New Layer for the Shadow
Create a new layer beneath the isolated object layer by clicking on the New Layer icon at the bottom of the Layers panel or using the shortcut Shift+Ctrl+N (Shift+Cmd+N on Mac). Name this layer “Shadow.”
Step 5: Transform the Shadow
With the “Shadow” layer selected, use the Elliptical Marquee Tool (M) or the Polygonal Lasso Tool (L) to draw the general shape of the shadow based on the light source direction. Fill this selection with black by using the Paint Bucket Tool (G) or pressing Alt+Backspace (Option+Delete on Mac).
Step 6: Blur the Shadow
To make the shadow look more natural, apply a Gaussian Blur. Go to Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur and adjust the radius until the shadow edges look soft and realistic. The exact value will depend on your image resolution and the intended shadow sharpness.
Step 7: Distort the Shadow
With the shadow layer still selected, go to Edit > Transform > Distort. Adjust the shadow’s perspective to match the light source’s angle and distance. You can also use Edit > Transform > Warp for more precise adjustments.
Step 8: Adjust Shadow Opacity
Lower the shadow layer’s opacity to blend it naturally with the background. Typically, an opacity between 40% and 70% works well, but this will vary based on your image.
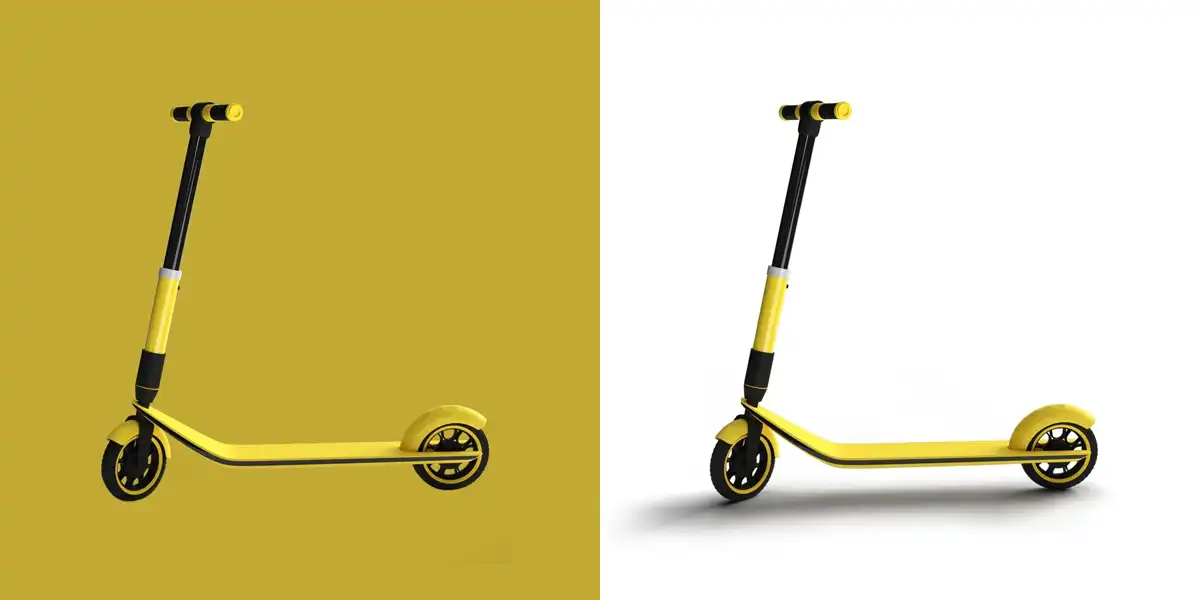

Enhancing Form Shadows
Step 9: Create Form Shadows
Form shadows add depth to the object itself. Select the object layer, and using the Burn Tool (O) set to Midtones, gently paint on the areas where the form shadow should be. This tool darkens parts of the image, creating a shadow effect.
Step 10: Refine the Shadows
Switch to the Dodge Tool (O) to lighten the areas where the light hits the object directly. This combination of the Dodge and Burn tools will create a more realistic three-dimensional effect.
Adding Advanced Shadow Effects
Step 11: Layer Styles for Shadows
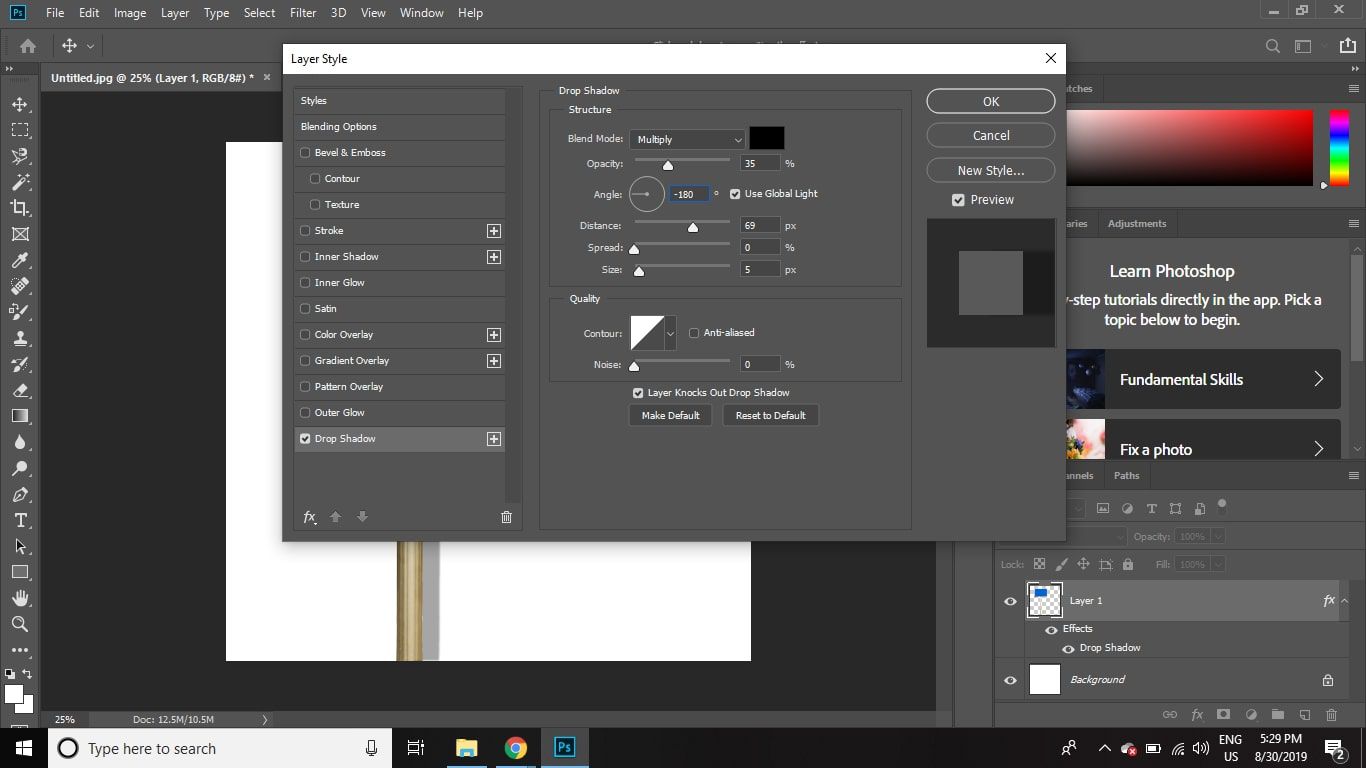
Another method for creating shadows is using layer styles. Right-click on the object layer and select Blending Options. Check the Drop Shadow box and adjust the settings like angle, distance, spread, and size to create a shadow. This method is quick and useful for simple shadow effects.
Step 12: Shadow Layer Masks
For more complex shadows, use layer masks. Add a mask to the shadow layer by clicking the Add Layer Mask icon at the bottom of the Layers panel. Use a soft brush to paint on the mask with black to hide parts of the shadow, creating a more realistic blend.
Final Adjustments
Step 13: Fine-Tune the Shadows
Once you have your shadows in place, take a step back and review your work. Make any necessary adjustments to the shadow’s blur, opacity, or shape. Pay attention to the overall lighting in your image and ensure the shadows are consistent.
Step 14: Color Matching
Shadows are rarely pure black. They often take on the color of the surrounding light. To color match your shadow, create a new layer above the shadow layer and set it to Color blend mode. Use a soft brush to paint the shadow with a color sampled from the environment.
Step 15: Save Your Work
Once satisfied with your shadow creation, save your work. Go to File > Save As and choose the desired format. For preserving layers, save as a PSD file. For sharing or printing, save as a JPEG or PNG.
Tips and Tricks
Practice Makes Perfect
Like any skill, creating realistic shadows takes practice. Experiment with different shadow types, angles, and lighting conditions to become proficient.
Study Real Shadows
Observe shadows in real life. Notice how they change with different light sources and angles. This will help you create more realistic shadows in your digital work.
Use References
When working on complex images, use reference photos to guide your shadow creation. This can be especially helpful when working on scenes with multiple light sources or intricate objects.
Keep It Subtle
In many cases, less is more. Subtle shadows can often be more effective than overly dark or harsh ones. Aim for a natural look that enhances the overall image without drawing too much attention to the shadow itself.
Leverage Photoshop Resources
Photoshop offers a plethora of tools and features that can assist in shadow creation. Explore blending modes, gradient tools, and custom brushes to add more depth and detail to your shadows.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Shadows Too Dark or Too Light
If your shadows appear too dark or too light, adjust the opacity and blend mode of the shadow layer. You can also use the Brightness/Contrast adjustment layer to fine-tune the shadow.
Shadows Not Blending Naturally
If your shadows aren’t blending naturally with the background, consider using the Smudge Tool (R) or a soft brush on a layer mask to soften the edges. Additionally, ensure your shadow color matches the environment.
Shadows Look Unnatural
Unnatural shadows often result from incorrect light source angles or shadow shapes. Reevaluate your light source and adjust the shadow accordingly. Using reference images can help you get the angles and shapes right.
Misaligned Shadows
Misaligned shadows can break the illusion of depth. Use the Transform tools (Distort, Warp, Skew) to realign and reshape the shadow so it appears naturally cast by the object.
Conclusion
Creating realistic shadows in Photoshop is a valuable skill that can enhance the depth and realism of your images. By following this step-by-step guide, beginners can develop a strong foundation in shadow creation. Remember to practice regularly, observe real-world shadows, and experiment with different techniques. With time and experience, you’ll be able to create stunning, lifelike shadows that bring your digital artwork to life.
Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, mastering shadows in Photoshop will undoubtedly improve the quality of your work and expand your creative possibilities. Happy editing!


